How To Find Scale Factor Of A Triangle
Scale Cistron
Calibration factor is a number by which the size of whatsoever geometrical figure or shape can exist changed with respect to its original size. It is used to depict the enlarged or reduced shape of any given figure and to find the missing length, surface area, or volume of an enlarged or reduced figure. It should be noted that the scale factor helps in changing the size of the figure and not its shape.
| 1. | What is a Calibration Factor? |
| 2. | Scale Gene Formula |
| iii. | How to Detect the Scale Factor? |
| 4. | FAQs on Calibration Factor |
What is a Scale Factor?
Scale factor is defined as the number or the conversion cistron which is used to modify the size of a figure without changing its shape. Information technology is used to increment or decrease the size of an object. The scale cistron can be calculated if the dimensions of the original figure and the dimensions of the dilated (increased or decreased) figure are known. For example, a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of ii units. At present, if we increase the size of this rectangle by a scale cistron of 2, the sides will become 10 units and 4 units, respectively. Hence, nosotros tin can use the scale factor to get the dimensions of the inverse figures.
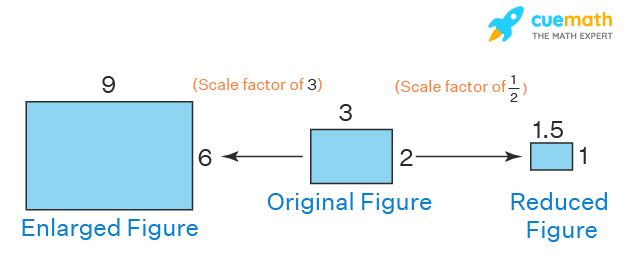
Observe the post-obit figure which shows how the scale factor can alter the original effigy to its larger and smaller versions. In the following figure, the original rectangle has the dimensions given as 3 units and ii units. To create an enlarged figure, the dimensions are multiplied by the scale factor of 3 using the formula: Dimensions of the new shape = Dimensions of the original shape × Scale cistron. This gives the new dimensions equally ix units and 6 units respectively. Similarly, to create a reduced figure, we multiply the original dimensions with the scale cistron of one/2. This gives the reduced dimensions as 1.5 units and i unit.
Calibration Gene Formula
The bones formula to notice the scale factor of a figure is expressed as,
Calibration gene = Dimensions of the new shape ÷ Dimensions of the original shape.
This formula can likewise exist used to summate the dimensions of the new figure or the original figure past simply substituting the values in the formula.
How to Notice the Calibration Factor?
The calibration gene tin be calculated when the new dimensions and the original dimensions are given. However, in that location are two terms that need to be understood when using the scale gene. When the size of a figure is increased, nosotros say that it has been scaled upwardly and when it is decreased, we say that it has scaled down.
Scale Up
Scaling upwardly means that a smaller figure is enlarged to a bigger ane. In this case, the calibration factor can be calculated by a formula, which is another version of the basic formula given in the previous section.
Scale factor = Larger effigy dimensions ÷ Smaller figure dimensions
The scale factor for scaling up is always greater than 1. For example, if the dimension of the larger figure is xv and that of the smaller ane is 5, let us place this in the formula which makes information technology: 15 ÷ five = iii. Thus, we can run across that the scale factor is greater than 1.
Scale Down
Scaling down means that a larger effigy is reduced to a smaller 1. Even in this instance, the calibration gene tin be calculated by a formula, which is another version of the basic formula.
Scale factor = Smaller figure dimensions ÷ Larger figure dimensions
The scale factor for scaling down is always less than ane. For example, if the dimension of the smaller figure is 8 and that of the larger one is 24, let u.s.a. place this in the formula which makes it: 8 ÷ 24 = 1/iii. Thus, we can see that the scale factor is less than one.
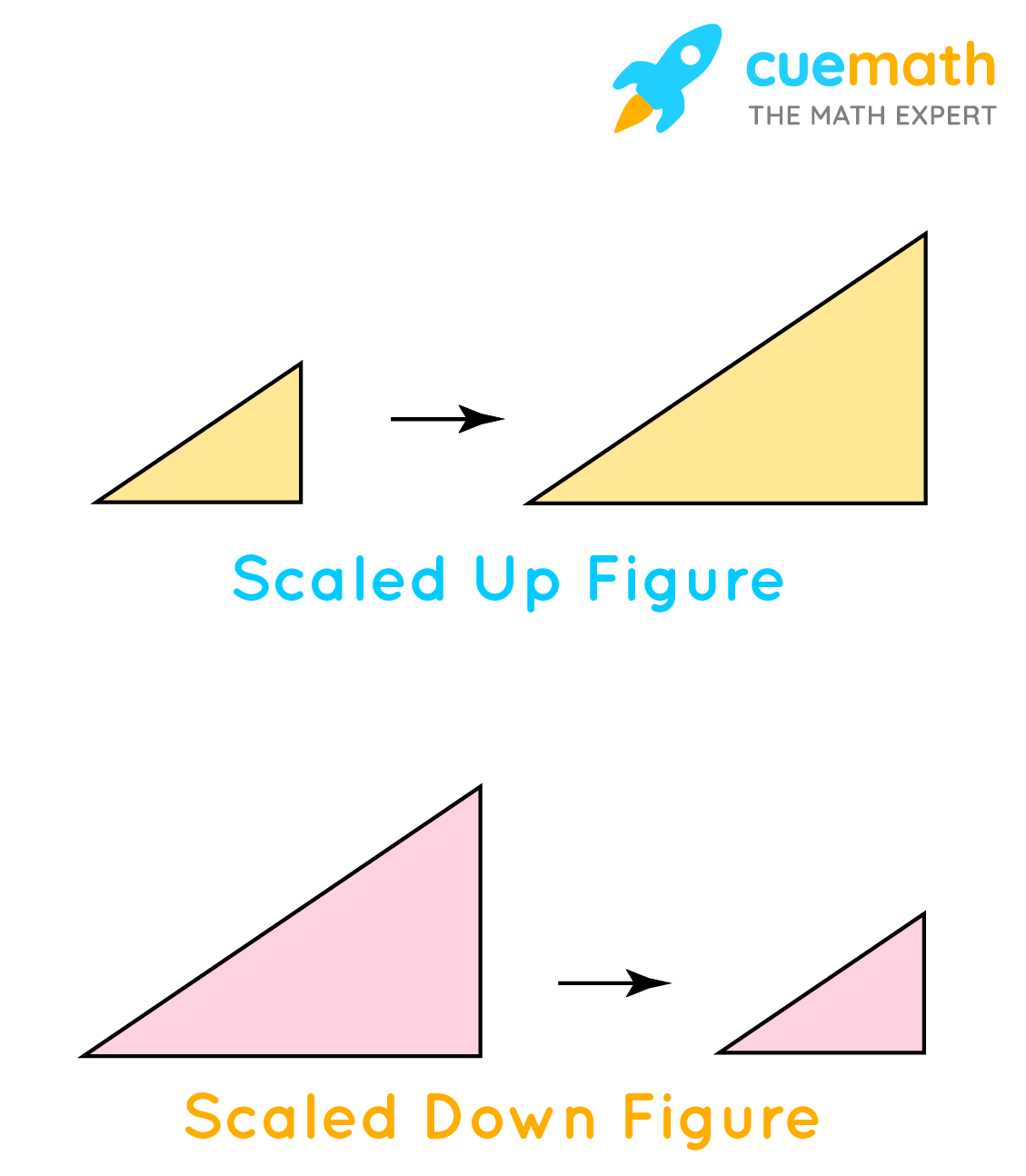
Observe the following triangles which explicate the concept of a scaled-upward figure and a scaled-downwardly figure.
Important Notes
The following points should be remembered while studying about the scale factor:
- The scale gene of a dilated figure is denoted by 'r' or 'k'.
- If the scale factor is more 1 (m > one), the image is enlarged.
- If the calibration factor is less than 1 (0< chiliad <1), the paradigm is contracted.
- If the scale factor is 1 (grand = 1), the paradigm remains the same.
- The scale cistron cannot be nothing.
☛ Related Manufactures
- Dilation Geometry
- Calibration Factor Worksheets 7th Grade
- Horizontal Scaling
- Vertical Scaling
Calibration Factor Examples
get to slidego to slidego to slide

Cracking learning in high school using simple cues
Indulging in rote learning, you are probable to forget concepts. With Cuemath, y'all will larn visually and be surprised by the outcomes.
Book a Free Trial Form
Do Questions on Scale Factor
become to slidego to slide
FAQs on Scale Factor
What is a Calibration Factor?
Scale cistron is a number that is used to draw the enlarged or reduced shape of any given figure. It is a number by which the size of whatsoever geometrical effigy or shape can be changed with respect to its original size. It helps in changing the size of the effigy but not its shape.
What Happens if the Scale Factor is Greater Than 1?
If the scale factor is more than 1 (k > one), it ways that the given figure needs to be enlarged.
What Does a Scale Factor of 0.5 Mean?
A scale factor of 0.5 means that the changed image will be scaled down. For example, the original figure of a square has one of its sides as 6 units. Now, let us apply the scale factor of 0.five, to change its size. Nosotros will use the formula: Dimensions of the new shape = Dimensions of the original shape × Calibration gene. Substituting the values in the formula: the dimensions of the new foursquare volition exist = half-dozen × 0.5 = iii units. This shows that a scale gene of 0.v changed the effigy to a smaller ane.
How exercise you Find the Calibration Factor?
The scale factor can be calculated when the new dimensions and the original dimensions are given. The bones formula to find the scale factor of a figure is: Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape. For example, if the side length of a foursquare is 6 units and if the size of the square has been increased such that the side length of the square becomes 18 units, let u.s.a. find the scale cistron. We will use the formula, Calibration factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape. After substituting the given values nosotros get, Scale gene = 18 ÷ 6 = iii. Therefore, the scale cistron that is used to increase the size of the foursquare is 3.
What Happens if the Calibration Factor is Less Than 1?
If the scale gene is less than i (0< k <1), and then the new epitome that is formed volition be contracted or scaled-down. In other words, the new effigy will have smaller dimensions as compared to the original effigy after information technology is resized using the scale gene which is less than 1.
Where do we Utilize a Scale Factor?
Scale factor is a number past which the size of whatsoever geometrical figure or shape can be changed with respect to its original size. When things are too big, nosotros employ calibration factors to calculate smaller, proportional measurements. It is used to compare two like geometric shapes and also in other fields like cooking, where the ingredients can exist reduced or increased according to the given state of affairs. Scale factor tin likewise exist used to find any missing dimensions in like figures.
What is the Formula For Scale Gene?
The basic formula that is used for calculating the scale gene is, Calibration factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape. In instance, if the original figure is scaled upwardly, the formula is written equally, Calibration gene = Larger figure dimensions ÷ Smaller figure dimensions. When the original figure is scaled downward, the formula is expressed as, Scale factor = Smaller figure dimensions ÷ Larger figure dimensions.
What Does a Negative Scale Factor Hateful?
A negative scale factor makes the dilation rotate 180° and it creates an epitome on the other side of the centre of the enlargement.
What Calibration Factor makes a Figure Smaller?
A scale factor which is less than 1 makes the original figure smaller. For example, let us use a scale gene of 1/3 to change the size of a figure with a given dimension of 36. We will place the given values in the formula: Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape. Substituting the values, we get, i/three = Dimension of the new shape ÷ 36. After solving this, the dimension of the new shape is = 12. Since 12 is smaller than 36, it ways the original effigy has been reduced in size. Thus, it can be seen that the scale factor which is less than one makes a figure smaller.
How is a Scale Different from a Scale Factor?
- Scale is a ratio that is used to define the relation of the actual effigy or object with its model. It is commonly used in maps to correspond the actual figures in smaller units. For instance, a scale of 1:iii means 1 on the map represents the size of 3 in the real world.
- Scale factor is a conversion factor - a number which is used to increment or subtract the size of a figure. For example, if a circle needs to exist increased in size using a scale gene of iv, and the circumference of the circle is 7 units. What volition exist the circumference of the new enlarged circle? We will use the formula, Calibration gene = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape. This can be written every bit, Dimension of the new shape = Calibration factor × Dimension of the original shape. After substituting the given values, we volition get, Dimension of the new shape = seven. After solving this, we get, Dimension of the new shape = 28 units.
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/geometry/scale-factor/
Posted by: romerofeliked.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How To Find Scale Factor Of A Triangle"
Post a Comment